We also revisited the idea of angles today.
Take a peek at this PBS video called, “What’s a 360?” Think about how a circle can be divided into 360/360. Each slice represented a rotation of 1 degree.
Why 360? Consider a few theories in the following video:
We then thought about what we have been learning about fractions, equivalent fractions, and… the clock. The clock was today’s very valuable multiple source. We started by thinking about the different ways a WHOLE clock is divided. We discovered that a WHOLE clock can be divided into:
- 2/2 (There are 2 sections, 1 for each half hour)
- 4/4 (There are 4 sections, 1 for each quarter hour.)
- 12/12 (There are 12 sections, 1 for each hour.)
- 60/60 (There are 60 sections, 1 for each minute.)
We then examined the angle of the clock’s hands when it is 3:00 p.m. When the minute hand is on the 12 and the hour hand is on the 3, the rays make a right angle or a 90 degree angle. We then connected this to our understanding for fractions – if we slice the clock into 4 pieces, the portion represented when it is 3:00 p.m. is 1/4 (one fourth).
- 1/4 = 3/12 = 15/60 = 90/360
- These are all equivalent.
- 90/360 represents the number of degrees (90 °) when it is 3:00 p.m.
We then looked at how many degrees each set of 5 minutes represents.
- 1/12 = 5/60 = 30/360
- These are all equivalent fractions.
- 30/360 represents the number of degrees (30°) when the hands are separated by 5 minutes (eg. 1:00 p.m.)
Finally, we looked at how many degrees each minute represented.
- 1/60 = 6/360
- These are equivalent fractions.
- 6/360 represents the number of degrees (6 °) when the hands are separated by 1 minute.
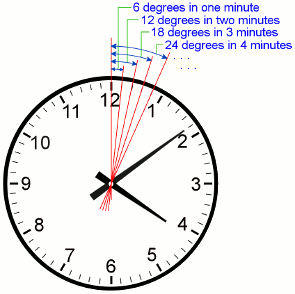
Based on what you know about fractions, equivalent fractions, and angles… what is the size of the angle represented on the clock above. How do you know?
As I started looking for video resources, I just couldn’t stop. There were so, SO many options for using this model to solve problems about fractions, angles, and time. Here are just few samples. As a scholar, definitely consider these multiple sources. Which one exercises your brain the most?
